Introduction to Medical Billing Services
Medical billing is the financial backbone of any healthcare practice, including small clinics, multi-specialty centers, and large hospitals. Without an efficient billing process, even the most skilled physicians and healthcare providers risk delayed payments, claim denials, and financial instability. Clinics, in particular, face unique challenges—they need to balance high-quality patient care with streamlined revenue cycle management.
At its core, medical billing is the process of translating healthcare services into standardized billing codes and submitting them to insurance providers for reimbursement. These reimbursements are crucial for a clinic’s survival, as they represent the majority of revenue in most healthcare practices.
Medical billing services—whether managed in-house, outsourced to professionals, or powered by advanced software—ensure that every patient encounter is correctly documented, coded, billed, and reimbursed. For clinics, this translates into fewer financial leaks, better compliance with healthcare regulations, and more time to focus on patient care.
But why is this topic so important now? Healthcare regulations, payer rules, and medical codes are constantly changing. Errors in billing can cause claim denials, compliance violations, and even legal issues. That’s why understanding medical billing services is not just an option—it’s a necessity for any clinic aiming for growth and financial stability.
Understanding the Medical Billing Process
The medical billing process is complex, with multiple steps that require accuracy and efficiency. Any misstep in this chain can cause delays in payment or outright denial of claims. Clinics that understand and optimize each step of the process have a significant advantage in managing their revenue cycle.
Patient Registration and Insurance Verification
The journey begins when a patient visits a clinic. During registration, staff must capture accurate demographic details, insurance information, and eligibility verification. Incorrect or incomplete information at this stage is one of the biggest causes of claim denials later on. A robust verification system ensures that the clinic knows whether a patient’s insurance plan covers the intended procedures before services are rendered.
Medical Coding Essentials (ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS)
Medical coding is the translation of healthcare services, diagnoses, and procedures into universal codes. These codes include:
- ICD-10 for diagnoses
- CPT for medical procedures
- HCPCS for supplies and services not covered under CPT
Coders must be meticulous—using the wrong code can lead to claim rejection, audits, and compliance issues. Clinics often employ certified coders or rely on billing companies to ensure accuracy.
Claim Submission and Reimbursement
Once coded, claims are submitted electronically through clearinghouses or directly to insurance payers. Timely submission is critical, as payers often have strict deadlines. After submission, the insurance provider processes the claim and reimburses the clinic based on the patient’s coverage plan.
Denial Management and Resubmission
Claim denials are inevitable in healthcare billing. Reasons may include incorrect coding, missing documentation, or payer-specific rules. Effective denial management requires quick identification of errors, correction, and resubmission. Clinics that lack a denial management strategy risk losing significant revenue.
Types of Medical Billing Services
Medical billing services can be structured in three ways depending on a clinic’s size, budget, and operational goals.
In-House Medical Billing
Some clinics prefer to manage billing internally with their own staff and software systems. This model offers greater control but requires continuous investment in training, software updates, and compliance management. In-house billing is usually more feasible for larger clinics with dedicated resources.
Outsourced Medical Billing
Outsourcing involves hiring third-party billing companies that specialize in healthcare revenue cycle management. This option reduces administrative burdens, minimizes errors, and ensures compliance with ever-changing regulations. Many small and medium-sized clinics prefer outsourcing because it’s cost-effective and allows them to focus on patient care.
Hybrid Billing Models
Hybrid models combine in-house management with outsourced support. For example, a clinic might manage patient registration and coding internally but outsource claim submissions and denial management. This model offers flexibility, allowing clinics to maintain some control while benefiting from external expertise.
Benefits of Medical Billing Services for Clinics
Medical billing services provide clinics with tangible benefits beyond just processing payments.
Faster Reimbursements and Reduced Errors
Efficient billing ensures that claims are submitted correctly and on time, leading to faster reimbursements. Automation and professional oversight also minimize human errors, which are the leading cause of claim denials.
Compliance with Healthcare Regulations
Healthcare regulations like HIPAA, ICD-10 coding standards, and payer-specific requirements are constantly evolving. Professional billing services stay updated with these changes, reducing compliance risks for clinics.
Cost Savings and Efficiency
Outsourcing billing often costs less than maintaining a full in-house team, especially for smaller clinics. Even larger clinics benefit from efficiency gains, reduced staff workload, and minimized denial rates.
Improved Patient Satisfaction
A smooth billing process reduces billing disputes, unexpected charges, and administrative hassles for patients. When patients have a seamless financial experience, their trust and satisfaction with the clinic increase.
Challenges in Medical Billing
While billing services are essential, clinics face several challenges that can affect efficiency and profitability.
Insurance Claim Denials
Denials remain one of the biggest hurdles in revenue cycle management. Clinics must establish strong denial management protocols to avoid revenue leakage.
Constant Regulatory Changes
From ICD code updates to new payer rules, regulations change frequently. Clinics that fail to keep up risk compliance violations and revenue loss.
Data Security and Privacy Issues
Billing involves sensitive patient data protected under HIPAA. Clinics must ensure robust cybersecurity measures to avoid breaches and penalties.
Staff Training and Knowledge Gaps
Medical billing requires ongoing education. Untrained staff may unintentionally submit incorrect claims, causing delays and compliance issues.
Medical Billing Software Solutions
Technology has transformed the way clinics handle billing, making processes faster, more accurate, and more transparent. Medical billing software plays a pivotal role in reducing human error, streamlining workflows, and ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations. For clinics of all sizes, investing in the right software can mean the difference between consistent cash flow and ongoing financial struggles.
Features of Modern Medical Billing Software
Today’s billing software offers a range of features designed to support every stage of the revenue cycle. Key features include:
- Automated claim submission and tracking – reducing manual effort and ensuring claims are submitted on time.
- Built-in coding assistance – helping staff choose the right ICD-10, CPT, or HCPCS codes.
- Eligibility verification tools – instantly checking insurance coverage before services are rendered.
- Denial management dashboards – making it easy to identify, correct, and resubmit rejected claims.
- Analytics and reporting – giving clinics insight into revenue trends, collection rates, and financial performance.
These tools not only reduce errors but also empower clinics with real-time data that supports smarter decision-making.
Cloud-Based vs On-Premise Systems
When selecting billing software, clinics often face the choice between cloud-based and on-premise systems.
- Cloud-Based Systems: Accessible from anywhere, updated automatically, and typically subscription-based. They require minimal IT infrastructure, making them popular among small to medium-sized clinics.
- On-Premise Systems: Installed locally and managed internally, offering more control but requiring higher upfront costs, maintenance, and IT staff. Large clinics with complex needs may prefer this model.
The decision usually comes down to budget, scalability needs, and security preferences.
Top Medical Billing Software Providers
Several providers dominate the market, offering solutions tailored to clinics of different sizes:
- Kareo – widely used by small clinics for its user-friendly interface.
- AdvancedMD – a robust solution offering integrated EHR and billing.
- Athenahealth – known for its powerful analytics and revenue cycle management tools.
- DrChrono – cloud-based with strong mobile accessibility.
- NextGen Healthcare – a popular choice for multi-specialty practices.
Selecting the right provider involves evaluating cost, features, and how well the system integrates with existing clinical workflows.
Outsourcing Medical Billing Services
Many clinics find that outsourcing their billing processes offers significant advantages over managing them in-house. However, this decision requires careful consideration.
Pros and Cons of Outsourcing
Pros:
- Reduced administrative burden on staff.
- Access to billing and coding experts.
- Lower error rates and faster reimbursements.
- Cost-effective compared to hiring full-time staff.
Cons:
- Less direct control over the billing process.
- Potential communication delays between clinic and billing company.
- Dependence on an external provider for revenue flow.
For most small to mid-sized clinics, the benefits often outweigh the drawbacks, especially when outsourcing to a reputable company.
How to Choose the Right Medical Billing Company
Selecting a billing partner is a critical decision. Clinics should consider:
- Experience and reputation in healthcare billing.
- Compliance record with HIPAA and payer rules.
- Transparency in reporting and communication.
- Technology used for claim tracking and analytics.
- Pricing model—whether it’s a flat fee or a percentage of collections.
A strong billing partner should feel like an extension of the clinic, not just a vendor.
Cost Structure of Outsourced Services
Outsourced billing companies typically charge 4%–10% of collections as their fee. While this may seem significant, it often proves cheaper than hiring, training, and retaining in-house staff. For small clinics, outsourcing is usually the most financially viable option.
Best Practices for Clinics to Optimize Billing
Even with software and outsourcing, clinics must adopt best practices to maximize efficiency and compliance in billing.
Staff Training and Education
Staff must be trained not only in coding and billing but also in patient communication about financial responsibilities. Well-trained staff minimize claim errors and enhance the patient experience. Clinics should invest in ongoing education programs and certifications for their teams.
Regular Audits and Compliance Checks
Routine internal audits help identify errors, ensure compliance with payer rules, and prevent fraud. Audits also highlight patterns of claim denials that can be corrected through process improvements.
Leveraging Automation and AI in Billing
AI and automation are revolutionizing billing. Examples include:
- AI-powered coding assistance that reduces errors.
- Predictive analytics to forecast denials and take preventive action.
- Automated reminders for patient payments and follow-ups.
These tools allow clinics to shift from reactive to proactive revenue cycle management.
The Role of Medical Coders and Billers
Behind every successful billing process are skilled coders and billers who ensure accuracy and compliance.
Responsibilities of Medical Coders
Coders review patient charts and assign the correct ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS codes. Their work requires deep medical knowledge and precision, as even minor mistakes can lead to denials or compliance issues.
Responsibilities of Medical Billers
Billers take coded information, prepare claims, and submit them to insurance companies. They also handle denials, patient billing inquiries, and collections. Essentially, they bridge the gap between clinical services and financial reimbursement.
Certifications and Training Requirements
Coders and billers often pursue certifications like CPC (Certified Professional Coder) or CPB (Certified Professional Biller) from AAPC. These credentials not only enhance their expertise but also reassure clinics of their professionalism and accuracy.
Legal and Compliance Considerations
Compliance in medical billing is non-negotiable. Clinics must adhere to strict legal frameworks to avoid fines, penalties, or loss of reputation.
HIPAA and Data Protection
Billing involves handling sensitive patient data. HIPAA requires clinics to implement safeguards to protect data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Medicare and Medicaid Compliance
Government insurance programs have their own billing requirements. Mistakes in billing these programs can trigger audits and penalties, so clinics must stay updated on evolving rules.
Avoiding Fraud and Abuse
Billing fraud—such as upcoding, unbundling, or billing for services not rendered—can result in severe consequences, including loss of license or criminal charges. Clinics must establish strong internal controls to ensure ethical billing practices.
Trends Shaping the Future of Medical Billing
The healthcare industry is evolving rapidly, and medical billing is no exception. Clinics that want to stay competitive must keep an eye on emerging trends and adopt them strategically.
Artificial Intelligence and Automation
AI-driven billing solutions are no longer futuristic—they’re here. From predictive analytics that anticipate claim denials to automated coding assistants, AI is transforming the speed and accuracy of billing. For clinics, this means reduced workloads, fewer human errors, and faster revenue cycles. Imagine a system that “learns” payer preferences and adjusts coding patterns accordingly—that’s the power of AI in medical billing.
Blockchain in Healthcare Billing
Blockchain technology offers transparency, security, and immutability in financial transactions. In billing, it can ensure that every transaction—whether between a patient, provider, or insurer—is recorded on a tamper-proof ledger. For clinics, blockchain may soon mean fewer disputes, quicker verifications, and improved trust with payers.
Telemedicine and Remote Billing Challenges
With telemedicine services becoming mainstream, billing has had to adapt. Remote consultations require different coding rules, and insurance coverage is still catching up. Clinics offering telehealth must ensure their billing processes are aligned with payer policies, or they risk delays and denials. As telemedicine grows, so will the demand for specialized billing practices.
Cost Analysis of Medical Billing for Clinics
Understanding the financial impact of billing services is critical for clinics of all sizes. Costs can vary widely depending on whether services are managed in-house or outsourced.
Hidden Costs of In-House Billing
While in-house billing gives clinics more control, it comes with hidden costs:
- Staff salaries, training, and turnover expenses.
- Software licensing fees and regular updates.
- Compliance costs to stay updated with changing regulations.
- Opportunity cost of staff time spent managing billing instead of patient care.
These hidden expenses can quickly outweigh the perceived savings of handling billing internally.
ROI of Outsourced Medical Billing
Outsourcing often yields a high return on investment. By reducing denial rates, accelerating reimbursements, and lowering administrative overhead, outsourced services can significantly improve cash flow. Clinics typically see a positive ROI within months of outsourcing, especially when working with experienced billing partners.
Small vs Large Clinic Billing Costs
- Small Clinics: Usually benefit most from outsourcing due to limited staff and resources.
- Large Clinics: May afford in-house billing but still face scalability challenges. Hybrid models often make the most sense here.
The key takeaway is that each clinic must assess its unique financial situation and choose the billing model that maximizes revenue while minimizing expenses.
Case Studies of Clinics Using Medical Billing Services
Real-world examples provide insight into how different clinics benefit from billing services.
Small Family Clinic Case Study
A small family clinic with limited staff struggled with claim denials and cash flow problems. After outsourcing billing, denial rates dropped by 40%, and reimbursement times improved significantly. This allowed the clinic to reinvest in patient care and expand services.
Multi-Specialty Clinic Case Study
A multi-specialty clinic using in-house billing found it difficult to manage the complexity of different specialties’ coding requirements. By adopting a hybrid model—keeping basic billing tasks internal while outsourcing specialty claims—they improved compliance and reduced errors without losing control.
Large Hospital-Based Clinic Case Study
A large hospital clinic implemented AI-driven billing software to handle high claim volumes. With predictive analytics, they reduced denials by 30% and improved overall collection rates. The integration also gave administrators real-time financial visibility.
These examples show that whether small or large, clinics can see measurable benefits from choosing the right billing model.
How to Implement Medical Billing Services in Your Clinic
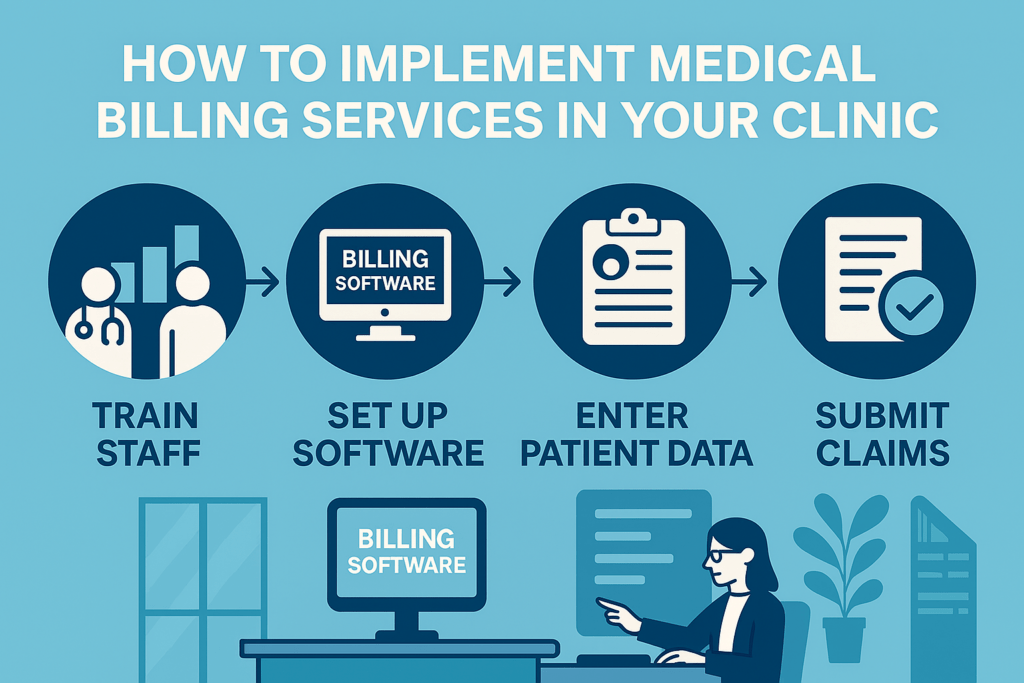
Transitioning to a new billing system or outsourcing provider requires careful planning.
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
- Assessment: Evaluate current billing challenges and needs.
- Decision: Choose between in-house, outsourced, or hybrid billing.
- Vendor Selection: If outsourcing or adopting new software, research and select the right partner.
- Integration: Ensure smooth data transfer and system integration.
- Testing: Run trial claims to identify issues before full rollout.
- Go Live: Transition fully to the new system or provider.
Staff Training and Transition Period
Staff buy-in is critical for success. Provide training sessions on new processes and tools. Expect a short adjustment period, but ensure support systems are in place to minimize disruptions.
Measuring Success and ROI
Success should be measured by:
- Reduced denial rates.
- Faster reimbursement times.
- Improved cash flow.
- Higher patient satisfaction with billing transparency.
Monitoring KPIs regularly ensures that the clinic gets the maximum value from its billing services.
Conclusion
Medical billing is far more than a back-office function—it’s the financial heartbeat of every clinic. Whether managed in-house, outsourced, or powered by advanced software, billing services directly impact revenue, compliance, and patient satisfaction.
Clinics that invest in the right billing strategy—combined with best practices, staff training, and emerging technologies—set themselves up for long-term success. With the healthcare landscape evolving, the ability to adapt billing processes will determine which clinics thrive and which struggle to survive.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between coding and billing?
Coding translates medical procedures and diagnoses into standardized codes, while billing uses those codes to prepare and submit claims for reimbursement.
2. How much does outsourced billing cost for clinics?
Outsourced billing usually costs between 4%–10% of collections, depending on the provider and services included.
3. How do billing errors affect clinic revenue?
Errors lead to claim denials, delayed payments, and compliance issues, all of which can significantly reduce a clinic’s revenue.
4. Can small clinics afford medical billing services?
Yes, outsourcing is often more affordable for small clinics than maintaining in-house billing staff and software.
5. What’s the future of medical billing in the next 5 years?
Expect more AI-driven automation, blockchain-based billing solutions, and specialized billing for telemedicine services.